Sensing, Measurement & Characterization Lasers
 What are Sensing, Measurement & Characterization Lasers?
What are Sensing, Measurement & Characterization Lasers?
Sensing, Measurement & Characterization Lasers are advanced laser systems (typically CW) designed specifically for a range of applications in fields such as machine vision, particle measurement, gas sensing, Raman spectroscopy, and interferometry. These lasers play a crucial role in providing accurate, high-resolution measurements and detailed characterization of various materials and phenomena. They provide researchers, engineers, and scientists with powerful tools to explore, measure, and understand the physical and chemical properties of materials, substances, and phenomena. Their versatility, accuracy, and non-invasive nature make them indispensable in a wide range of scientific, industrial, and research applications.
Have questions?
Sensing, Measurement & Characterization Applications
Interferometry Lasers: Interferometers are optical devices that utilize the interference of superimposed electromagnetic waves to extract information about the test target. Interferometry lasers (typically CW, SLM, single-mode, UV, violet, blue, green, yellow, red) are used in interferometric applications, exhibiting long coherence length characteristics, which are necessary for accurate measurements.
Machine Vision Lasers: Machine vision refers to the process of utilizing active imaging technologies to automate inspection and analysis for process control and robot guidance in industrial applications. Machine Vision Laser sources (typically CW, visible or IR) provide a means for data collection and analysis, feedback for automatic or manual adjustments, or simply throwing a warning light or even stopping the system.
Particle Measurement Lasers: Particle measurement is widely deployed as a means for counting and sizing the number of particles in both air and fluids in optical particle counting and dynamic light scattering applications for example. These lasers (typically CW or ns pulsed, IR) must then have a high-quality continuous-wave TEM00 laser. Otherwise, the speckle pattern of the multi-mode beam will interfere with the measurement of the scattered light.
Raman Spectroscopy Lasers: (CW & ps or fs pulsed, SLM, single/multimod, UV, violet, blue, green, yellow, red) Raman Spectroscopy is an analytical technique, studying the vibrational modes of molecules, used to identify and quantify the chemical composition and molecular bond structure of a sample by the analysis of scattered light. Raman spectroscopy lasers are typically wavelength stabilized VBG laser diodes or single-frequency DPSS lasers, which allows for accurate wavelength shift (Raman shift) measurements, critical to Raman Spectroscopy.
Gas Sensing Lasers: Gas sensing lasers are often distributed feedback lasers (DFB) or distributed Bragg reflector lasers (DBR), widely used as gas sensing lasers (typically diodes, SLM, IR or SWIR) due to their ability to be frequency tuned while maintaining single mode operations. Tunable diode laser spectroscopy (TDLS) can measure the concentration, temperature, and pressure of various gases in-situ under harsh conditions with good time resolution, sensitivity, and selectivity.
Recommended Laser Series
We recommend the following laser series options for Sensing, Measurement & Characterization applications. There can often be a ton of options and many variables. Contact us today for help finding the perfect laser for your specific application!
Have questions?

 SHIPS TODAY
SHIPS TODAY  What are Sensing, Measurement & Characterization Lasers?
What are Sensing, Measurement & Characterization Lasers?







 The REP series includes high-performance, tunable, single-frequency (DFB-like) diode lasers and Fabry-Perot laser diodes in wavelengths from 760nm thru 2350nm, designed to address challenges in Gas Sensing, LIDAR, Spectroscopy, and Telecom. The REP series includes high-power and narrow linewidth options, covering various product ranges at the most popular wavelengths, providing customizable units with multiple packaging options, including the Fiber coupled 14-pin butterfly, TO39 (w/TEC), and TO56.
The REP series includes high-performance, tunable, single-frequency (DFB-like) diode lasers and Fabry-Perot laser diodes in wavelengths from 760nm thru 2350nm, designed to address challenges in Gas Sensing, LIDAR, Spectroscopy, and Telecom. The REP series includes high-power and narrow linewidth options, covering various product ranges at the most popular wavelengths, providing customizable units with multiple packaging options, including the Fiber coupled 14-pin butterfly, TO39 (w/TEC), and TO56.
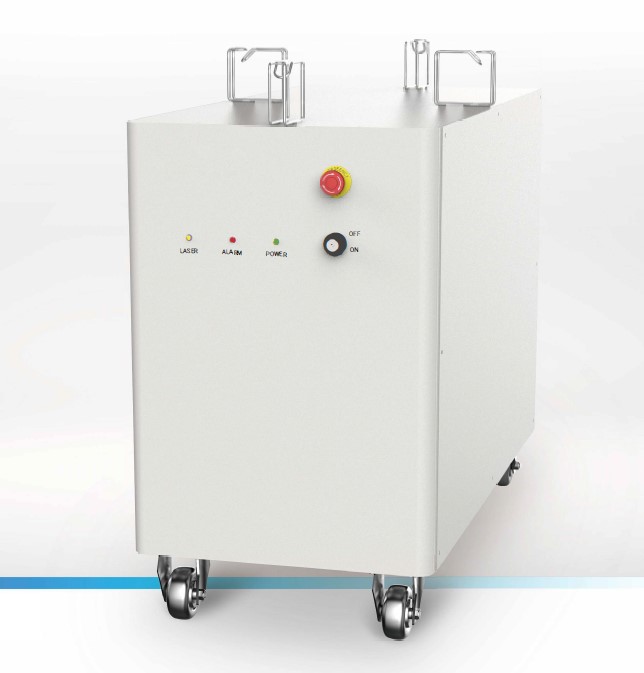 The RPKBDL Series is a high-power direct diode turn-key system available in wavelengths of 445nm, 915nm, or 976nm, providing up to 3kW of power and unprecedented brightness. Its pluggable design makes maintenance easy, avoiding troubles and high time costs caused by return-to-factory maintenance. The RPKBDL series results from continuous innovation, ensuring high technical strength and product quality. This highly customizable system allows us to meet our customers’ specific needs, providing high-quality products at reasonable prices.
The RPKBDL Series is a high-power direct diode turn-key system available in wavelengths of 445nm, 915nm, or 976nm, providing up to 3kW of power and unprecedented brightness. Its pluggable design makes maintenance easy, avoiding troubles and high time costs caused by return-to-factory maintenance. The RPKBDL series results from continuous innovation, ensuring high technical strength and product quality. This highly customizable system allows us to meet our customers’ specific needs, providing high-quality products at reasonable prices.
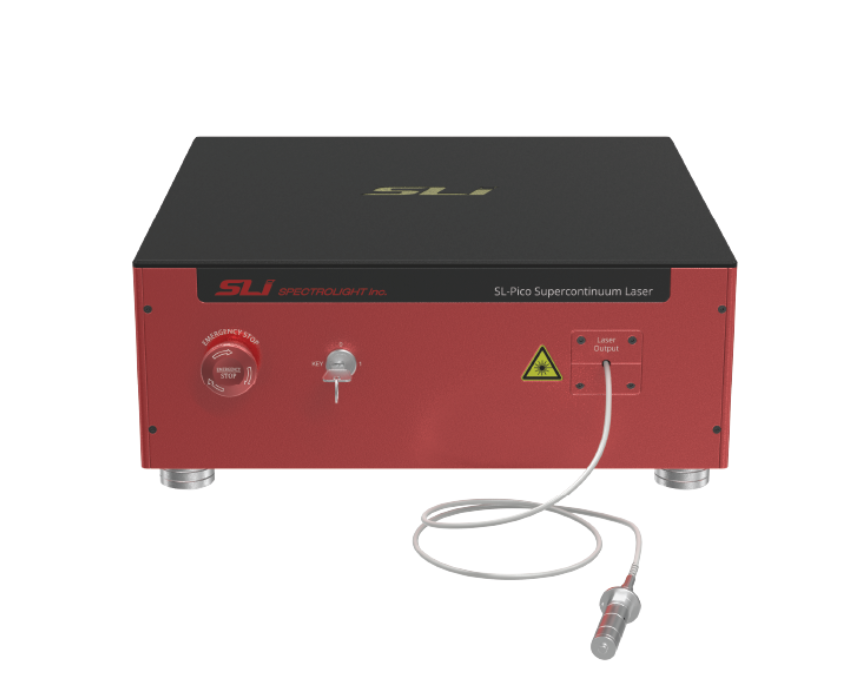
 The SL-Pico series of picosecond supercontinuum lasers is designed to meet the diverse and dynamic needs of cutting-edge research and industrial applications. These supercontinuum white lasers are highly regarded for their wide wavelength range and cost-effectiveness. The SL-Pico offers a spectral range from 410 to 2400 nm, has high power, is very stable, and is capable of delivering power up to 8 W. The SLM versions are mode-locked fiber lasers with a fixed rep. rate, and the SLMV versions have a tunable repetition rate (up to 40 or 200 MHz), ensuring compatibility with a wide range of devices and various applications like fluorescence microscopy, TCSP, hyperspectral imaging, semiconductor inspection, and much more!
The SL-Pico series of picosecond supercontinuum lasers is designed to meet the diverse and dynamic needs of cutting-edge research and industrial applications. These supercontinuum white lasers are highly regarded for their wide wavelength range and cost-effectiveness. The SL-Pico offers a spectral range from 410 to 2400 nm, has high power, is very stable, and is capable of delivering power up to 8 W. The SLM versions are mode-locked fiber lasers with a fixed rep. rate, and the SLMV versions have a tunable repetition rate (up to 40 or 200 MHz), ensuring compatibility with a wide range of devices and various applications like fluorescence microscopy, TCSP, hyperspectral imaging, semiconductor inspection, and much more! The SMX Series of US-made, high-power, thermally stable, and cost-effective InP laser diodes is available at 13XX, 14XX, 15XX, 16XX, and 19XX nm, perfect for medical, military, aerospace, LIDAR, free-space communications, and more! With a patented EPI structure, low-cost packaging, DFB & SOA configurations, ISO certified supply chain with full lifecycle traceability, focus on ease of integration, and custom design capabilities, this laser diode family is an excellent choice for reliable, high-power InP devices.
The SMX Series of US-made, high-power, thermally stable, and cost-effective InP laser diodes is available at 13XX, 14XX, 15XX, 16XX, and 19XX nm, perfect for medical, military, aerospace, LIDAR, free-space communications, and more! With a patented EPI structure, low-cost packaging, DFB & SOA configurations, ISO certified supply chain with full lifecycle traceability, focus on ease of integration, and custom design capabilities, this laser diode family is an excellent choice for reliable, high-power InP devices.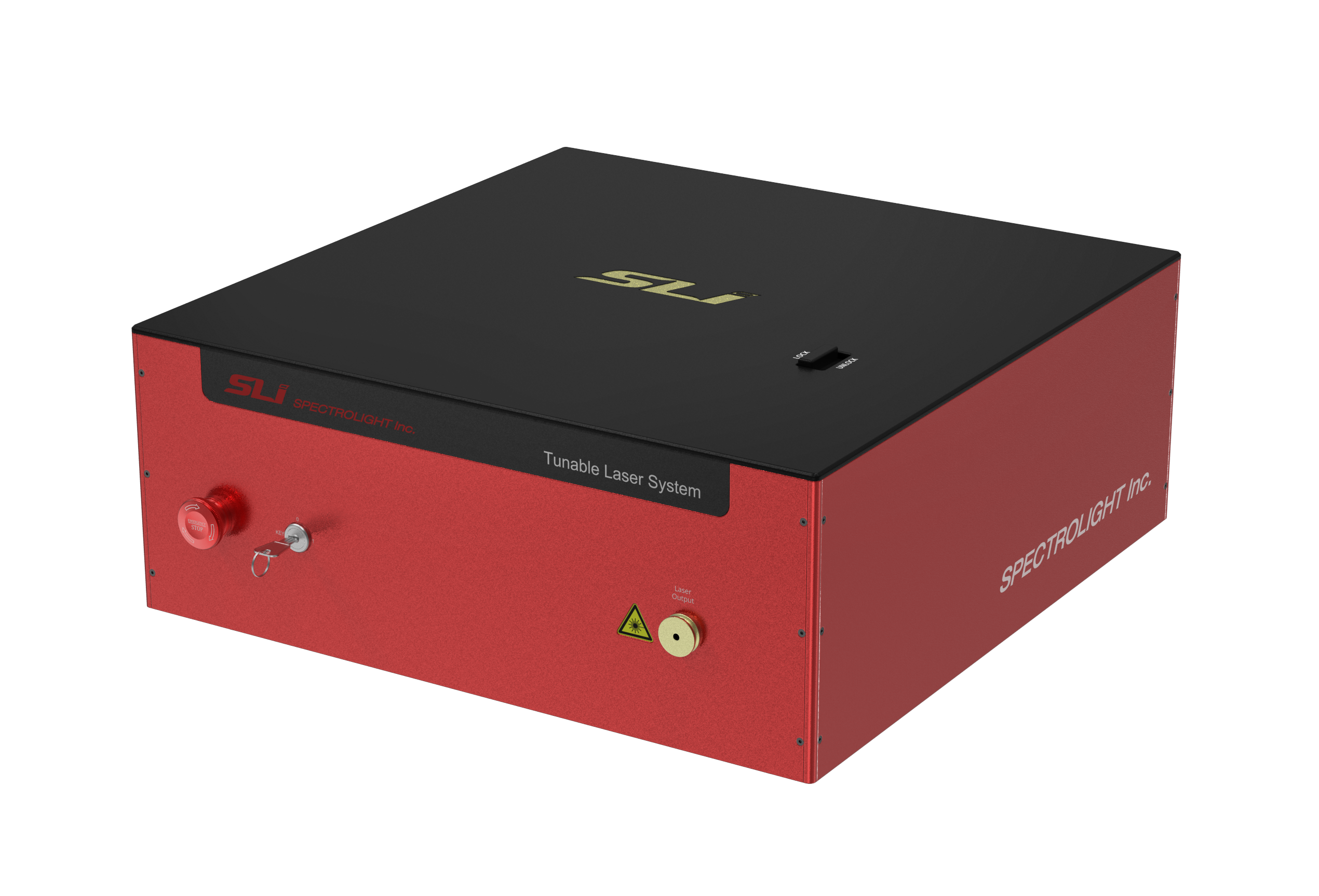 The TLS series is the broadest continuously optically tunable broadband picosecond laser combining a supercontinuum laser & tunable bandpass filter. Users can tune output power, wavelengths from 410-1700nm by choosing the VIS, IR, SWIR, or a custom configuration, and real-time bandwidth control for TLS-Red (10 or 20nm fixed for TLS-Blue). These picosecond tunable lasers are suitable for various fields that require precision scanning and high output from fluorescence microscopy to time-resolved spectroscopy, such as TCSPC, Hyperspectral imaging, Machine vision, Semiconductors, Sensors, and other applications.
The TLS series is the broadest continuously optically tunable broadband picosecond laser combining a supercontinuum laser & tunable bandpass filter. Users can tune output power, wavelengths from 410-1700nm by choosing the VIS, IR, SWIR, or a custom configuration, and real-time bandwidth control for TLS-Red (10 or 20nm fixed for TLS-Blue). These picosecond tunable lasers are suitable for various fields that require precision scanning and high output from fluorescence microscopy to time-resolved spectroscopy, such as TCSPC, Hyperspectral imaging, Machine vision, Semiconductors, Sensors, and other applications. The uniMir Series is a long-wavelength, single-frequency, DFB, CW Quantum Cascade Laser based on proprietary technology. The technology’s versatility allows them to address various wavelengths between ≈ 10-14um and 17-19um. Now commercially available in a sealed High Heat Load (HHL) package, with integrated collimating lens, thermistor, and thermoelectric cooler (TEC), well suited for integration into systems, or as a stand-alone turnkey system for R&D and detection applications.
The uniMir Series is a long-wavelength, single-frequency, DFB, CW Quantum Cascade Laser based on proprietary technology. The technology’s versatility allows them to address various wavelengths between ≈ 10-14um and 17-19um. Now commercially available in a sealed High Heat Load (HHL) package, with integrated collimating lens, thermistor, and thermoelectric cooler (TEC), well suited for integration into systems, or as a stand-alone turnkey system for R&D and detection applications. The VaryDisk Series is a versatile family of thin-disk laser systems that provide high pulse energies at high average powers and are suitable for lab or industrial use. These thin-disk regenerative amplifiers offer a range of output specifications to fit various application needs. The base configurations provide 25 W average power with 2.5 mJ pulse energy @ 343 nm (THG), 50 W and 5 mJ @ 515 nm (SHG), and 100W and 100 mJ @ 1030 nm.
The VaryDisk Series is a versatile family of thin-disk laser systems that provide high pulse energies at high average powers and are suitable for lab or industrial use. These thin-disk regenerative amplifiers offer a range of output specifications to fit various application needs. The base configurations provide 25 W average power with 2.5 mJ pulse energy @ 343 nm (THG), 50 W and 5 mJ @ 515 nm (SHG), and 100W and 100 mJ @ 1030 nm.