Microchip laser technology is a perfect option for various LIDAR-based applications, as well as LIBS, spectroscopy, micromachining, and more. Microchip lasers are typically compact and lightweight, allowing for easier and more efficient integration in airborne and portable, handheld applications, and the laser characteristics are in line with LIDAR requirements for collecting good data.
LIDAR & 3D Scanning
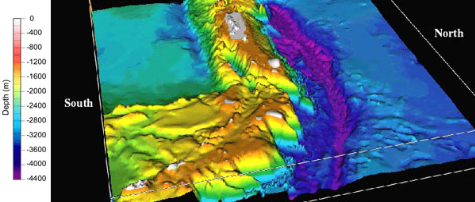
LIDAR, an acronym for light detection and ranging, is an optical analog to traditional radar (radio detection and ranging). Utilizing time-of-flight (ToF), linear frequency modulation (LFM), quasi-random phase matching and other measurement methods, LIDAR laser systems can calculate the distance to an object, the velocity of that object, composition and flow rate of a medium, and create three-dimensional digital representations of an object or area. LIDAR technologies provide higher bandwidth signals and substantially improved, high resolution detection, compared to traditional radio waves, due to the greatly increased optical frequencies. While LIDAR is typically referring to distance and velocity measurements (e.g. autonomous vehicles, or wind turbine monitoring), or mapping (e.g. bathymetric & airborne topographic LIDAR or 3D mapping), 3D laser scanning focuses on smaller, close-proximity objects and environments, creating a point cloud of data for digital reconstruction in 3D space for prototyping, reverse engineering, virtual & augmented reality, industrial design, and more.
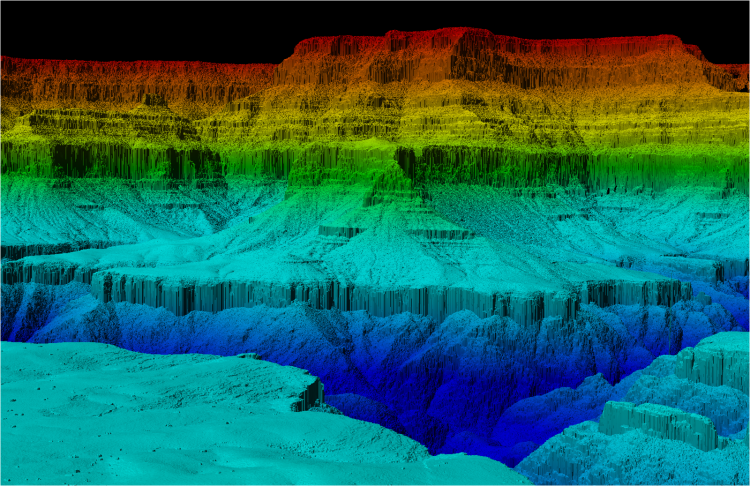
Laser Sources for LIDAR & 3D Scanning
LIDAR lasers are available in a vast range of configurations, tailored for different sets of end-use applications. The main determining factor for which type of LIDAR laser you need depends on whether your application is measuring a moving or stationary target. If your target is stationary, and distance is the only necessary measurement, short-pulsed lasers, with pulse durations of a few nanoseconds (even <1ns, into the picosecond range) and high pulse energy are what you’re looking for. This is also accurate for 3D scanning applications (given a stationary, albeit a much closer target), but select applications can also benefit from frequency-modulated, single-frequency (narrow-linewidth) fiber lasers. If your target is moving, and speed is the critical measurement, you need a single-frequency laser to ensure accurate measurement of the Doppler shift.

While the primary difference between traditional LIDAR and 3D scanning applications is the distance from the laser to the target, both sets of applications benefit from the features provided by high-quality microchip lasers. Lightweight and very compact modules, with low power draw, are perfect for integrating into portable devices for long battery life and increased mobility in the field. Excellent beam quality enables very small spot sizes and therefore, high peak power, incident upon the sample, for high-quality data collection. A simplistic design and low cost ensure a long lifetime of reliable performance, with reduced susceptibility to shock and vibration, without breaking your budget.
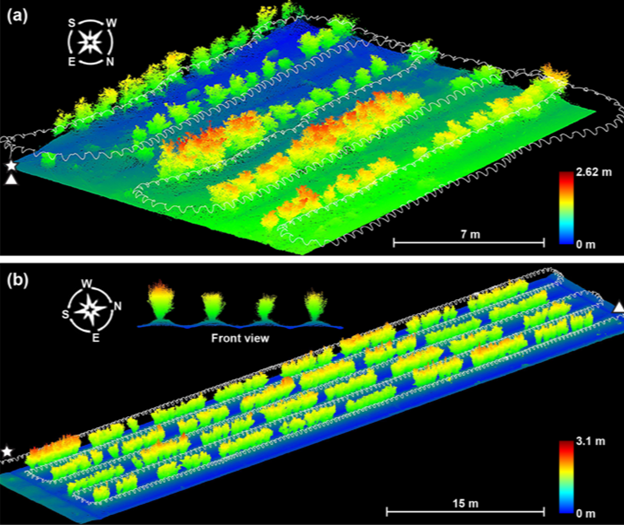
Microchip Lasers for LIDAR Based Applications
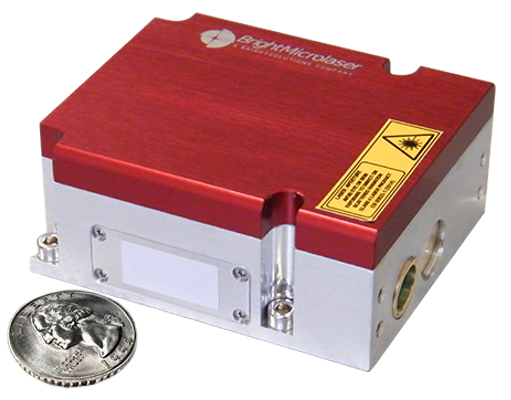
The SB1 Microchip laser module series from Bright Microlaser, provides all the features you need for a successful, low-cost, compact, and reliable OEM LIDAR solution. These diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) microchip lasers are available in several standard configurations, in wavelengths of interest for LIDAR applications (532nm & 1064nm), with output power up to 400 mW, pulse energies up to 80µJ, and pulse widths from a few nanoseconds down to 350ps. These microchip lasers use a saturable absorber passive q-switch, with factory-set repetition rate from single shot to 100kHz. Utilizing a passive q-switch means you don’t need an extra driver, allowing for a cheaper and more compact design. Read more about passive vs. active q-switching. The single longitudinal mode (SLM) SB1 series exhibits single-frequency operation, producing narrow linewidths, with high-quality beam output (M2 <1.3), and a pulse to pulse instability of <3%.

See the SB1 Microchip Laser Series
In addition to the excellent optical performance, these ultra-low SWaP microchip lasers are rugged and reliable, with improved shock and vibration resistance, and have even been space-qualified, with one of these units integrated into NASA’s OSIRIS-REx space mission. Based on customer feedback, these microchip laser modules have been completely re-designed into a simple All-in-One package with integrated drivers and electronics, allowing for a consistent and easily interchangeable form factor across all configurations. Eliminating needless components, reducing cost, size, weight, and complexity, and adding a new & improved user interface, these modules are easier to use and integrate, while keeping the same outstanding performance our customers demand. Furthermore, customization options are also available to meet customer’s unique requirements, opening the door to the most demanding applications, whether it be space-based LIBS, aerospace LIDAR, 3D scanning on construction sites, or UAVs !
Many industries take advantage of LIDAR and 3D scanning applications:
- Agriculture: LIDAR is used to map terrains, or to tell farmers where they should be distributing their costly fertilizers
- Automotive: LIDAR is used for obstacle detection and avoidance
- Biology & Conservation: LIDAR is used to monitor forest canopy heights or deforestation
- Atmospheric Remote Sensing & Metrology: LIDAR is used to measure winds, study clouds, or aerosols
- Military: LIDAR for autonomous vehicle guidance and for identifying possible targets
- Mining: LIDAR is used to map excavated areas to determine volume removal
- Surveying: LIDAR is used for mapping building and surrounding areas for future development
Talk to a knowledgeable Product Manager today by Contacting Us here, or by calling us at info@rpmclasers.com!
See ALL the lasers we offer for LIDAR and 3D Scanning Applications:
Check out some of our other LIDAR Articles:
|
Blog: Bathymetric and Topographic LIDAR
|
Blog:
|
Whitepaper:
|

 SHIPS TODAY
SHIPS TODAY