Technically speaking fiber lasers are a specific subset of diode-pumped solid-state lasers (DPSS), even though their unique qualities tend to get them placed in their own category. As a diode-pumped laser, fiber lasers take advantage of the shape of the dopant’s absorption spectrum in order to maximize the efficiency by pumping at the wavelength of peak absorption. The most well-known example of this is the 808 nm absorption peak on neodymium (Nd) which is exploited in traditional Nd:YAG /Nd:YVO DPSS lasers. In this blog post we are going to take a look at two most commonly used fiber laser dopants erbium (Er) and ytterbium (Yb) which both have a strong absorption peak at 976 nm, but who’s bandwidths vary dramatically causing one to require a wavelength stabilized diode pump.
The two figures below show the absorption spectra for Er on the left and Yb on the right, over roughly the same spectral region (approximately 875 nm to 1050 nm). From these two spectra, it is obvious that while their peak locations are in the same place, the spectral bandwidth of Yb dopant is at least an order of magnitude narrower. As a result, using a traditional high-power fiber-coupled diode laser, which would typically have a full-width half max (FWHM) linewidth of approximately 6 nm would never work for Yb. But, by comparison, this would be more than acceptable for pumping an Er-doped fiber laser.
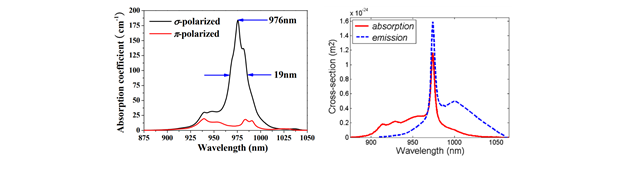
Fortunately, RPMC offers both traditional Fabry–Pérot diode lasers and volume Bragg grating (VBG) wavelength stabilized diode lasers. In order to achieve wavelength stabilization, the front facet of the diode is coated to lower the reflectivity and therefore increasing the gain threshold across all possible lasing wavelengths, then the VBG is placed in front of the diode to serve as the output coupler. This causes the laser gain threshold to be reduced only at the specific wavelength which meets the Bragg condition, therefore only allowing lasing at that specific wavelength. Additionally, this approach eliminated the diode lasers tendency to slightly shift wavelength with fluctuations in temperature and current. These small shifts in wavelength cause negligible effects in Er-doped fiber lasers, but can be detrimental to Yb doped fiber lasers.
Here at RPMC, we offer a selection of wavelength stabilized 976 nm fiber laser pumps, available with output powers ranging from 3 W to 400W, ideal for Yb-doped fiber laser pumping. For detailed technical specifications on both our Fabry–Pérot and VBG stabilized 976 nm (and other wavelengths) fiber lasers pump lasers.
Talk to a knowledgeable Product Manager today by Contacting Us here, or by calling us at info@rpmclasers.com!

 SHIPS TODAY
SHIPS TODAY 