At RPMC we offer one of the widest ranges of laser diodes on the market, and if you have been following us for some time now, we often mention that we offer both single emitters and arrays (bars). In this blog post we are going to take a look at exactly what we mean when we talk about diode bars, but in order to do that, we need to first take a small detour and talk about the role of the ridge waveguide in laser diodes in general.
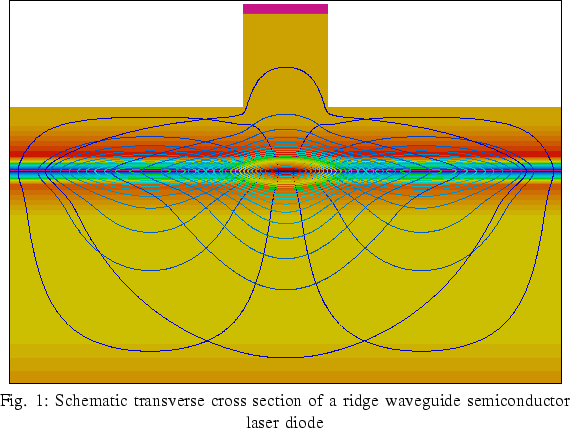
Most people reading this article probably have a general understanding of the fact that the photons in a laser diode are generated by electron-hole recombination at the PN junction inside of the diode, and that the front and back facets of the diode serve as the optical resonator. While this analysis of how a laser diode works is more than effective for gaining a basic understanding of its make-up, the ridge is a critical element is often left out of any fundamental discussion. The ridge, as shown in the simulation below serves as a step-index waveguide ensuring that all of the light emitted from the PN junction is contained and traveling in the proper direction. By adjusting the width of the ridge, an engineer can control various properties of the laser particularly the power, mode structure, and modulation speed (capacitance), making it one of the most important factors in a laser diodes design.
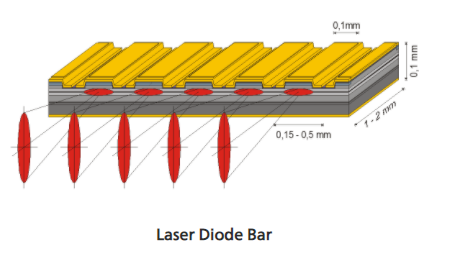
The vast majority of laser diodes only contain a single ridge (we call these single emitters), but for very high power laser applications it became helpful to create diode structures with multiple ridges in order to increase the total power output without increasing the total power density on the facet. This multi-ridge structure is what is known as a diode array or diode bar, and can contain as many as 100 emitters in a single structure producing over 300 watts of power. The figure below shows a typical structure of a laser diode array.
For even higher power applications these bars can be stacked and put into a single package capable of producing kilowatts of laser power. In this case, microchannel cooling is often used in laser diode bar stacks due to a large amount of waste heat in a small area. Laser Diode Bars and Stacks are available in several free space and fiber coupled packages. Here at RPMC we offer a wide variety of high power diode stacks from both Jenoptik and FocusLight. Depending on the output power and package cooling these laser can either be run in continuous wave (CW) or quasi-continuous wave (QCW) operation.
These high power laser diode stacks are often used in applications ranging from materials processing such as welding, cutting, and cladding, to medical applications such as hair removal and ophthalmology.
For detailed technical specifications on our laser diode bars and stacks click here or talk to one of our laser experts today by calling 1-636-272-7227.
Additionally, if you want to learn more about laser fundamentals check out our Lasers 101 laser selection guide.

 SHIPS TODAY
SHIPS TODAY 