One of the most challenging tasks in any aerial combat situation is determining which assets on the ground to target and which ones to avoid. This determination is particularly challenging when enemy assets are camouflaged or hidden amongst civilian assets. Because of this challenge, a practice, commonly referred to as “painting the target,” was developed and has been successfully deployed for many years, allowing ground forces to identify and designate targets for successful engagement by aerial support.
Of course, on the modern battlefield, soldiers aren’t marking targets with cans of spray paint for pilots to try to locate. Instead, they use portable laser designator systems, designed to illuminate the target with infrared radiation, which is then easily detected and tracked by their aerial counterparts. In this application note, we will examine the critical laser requirements for laser designation systems and discuss what types of lasers are ideal for these systems.
Target Designation Laser Source Requirements – Applications
There are many different types of laser designation systems used by the military today, from tracking small payloads to hand-launched UAS, high-flying planes, portable targeting, rifle-mounted targeting & much more. Still, they all share the same basic functionality and outcome. In a laser designation system, an infrared laser is fixed onto a target of interest and pulsed with a predetermined frequency code. This frequency code allows the infrared receiver on the plane or missile to efficiently recognize and lock onto the pulsed signal, scattered off the target, which enables the effective delivery of the projectile on target. At a glance, the laser requirements seem relatively straightforward. The laser needs to be invisible to the human eye, and it needs to have a programmable pulse rate. Still, when you look in more detail, many small factors add up to big problems if not appropriately addressed.
Target Designation Laser Source Requirements – Laser Divergence
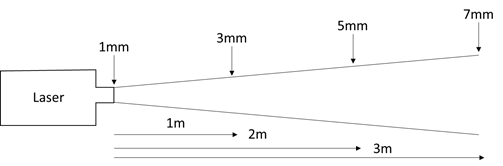
According to the NATO standard STANAG 3733, the laser beam divergence must be small enough that 90% of its energy is incident upon the target for 95% of the time, assuming a target size of 2.3m2. Ideally, a soldier would be positioned at a safe distance (up to 5km away) from the designation target. Given this great distance, it is critical that the laser source has excellent beam divergence and pointing stability ratings. For example, if a laser beam has a half-angle divergence of 1 mrad, its radius will expand at a rate of 1 mm per meter. While this slight increase in radius may not seem like much, at a distance of 2km, an initial laser beam diameter of 1 mm will have expanded to 4 meters in diameter at the target. The figure below gives a visual representation of how rapidly a laser with a half-angle divergence of 1 mrad can balloon in size. This rapid divergence is problematic when locking onto smaller targets without more than 10% of the light missing the mark. Furthermore, it dramatically reduces the overall intensity of the reflected light, making it harder to be detected by the missile’s targeting system. Similarly, problems can arise regarding the laser’s pointing stability, given that any minuscule variations in beam angle at the source can result in massive variances of the beam’s position at a distance. These significant variances in beam position can be devastating when trying to meet the 95% stability requirement also laid out in the NATO standards.
Target Designation Laser Source Requirements – Repetition Rate (PRR)
The accuracy of the pulse repetition rate is another critical property that one must consider. The infrared receiver on the plane or missile must confirm that the illuminated target matches the predetermined frequency code. Otherwise, the guidance system will not be able to lock on, regardless of the signal’s brightness. Therefore, if there is jitter in the pulse triggering, the frequency and timing can be altered, distorting the frequency code and hindering the receiver’s ability to confirm the signal. Lastly, in addition to the optical considerations laid out in the last paragraph, ruggedization, miniaturization, and power consumption requirements for the laser are equally important. Having reliable tools, built to withstand vibration and shock, and designed with low SWaP in mind – to be easily integrated with various equipment, where space and resource constraints limit your options – is key to mission success.
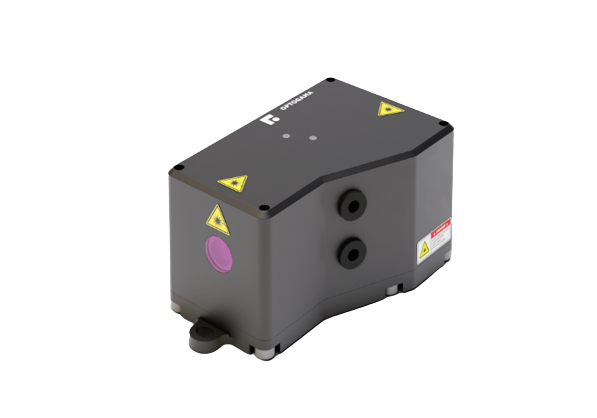 Optogama specializes in “eye-safe” 1.54 µm Erbium Glass Lasers and custom laser components, offering reliable, compact, and low SWaP (Size, Weight, and Power) solutions for airborne, handheld, and portable applications. Known for rugged, MIL-compliant designs, Optogama’s lasers provide high pulse energies with nanosecond pulse widths, ensuring cost-effective performance in harsh environments. Their products include standard and custom lasers, optical components, and nonlinear crystals, with an emphasis on easy integration and tailored configurations to meet diverse application needs. With a focus on quality and innovation, Optogama delivers reliable, high-performance solutions backed by ISO9001 standards and a decade of photonics expertise. Whether for research labs or field applications, Optogama’s laser systems are engineered for longevity and precision.
Optogama specializes in “eye-safe” 1.54 µm Erbium Glass Lasers and custom laser components, offering reliable, compact, and low SWaP (Size, Weight, and Power) solutions for airborne, handheld, and portable applications. Known for rugged, MIL-compliant designs, Optogama’s lasers provide high pulse energies with nanosecond pulse widths, ensuring cost-effective performance in harsh environments. Their products include standard and custom lasers, optical components, and nonlinear crystals, with an emphasis on easy integration and tailored configurations to meet diverse application needs. With a focus on quality and innovation, Optogama delivers reliable, high-performance solutions backed by ISO9001 standards and a decade of photonics expertise. Whether for research labs or field applications, Optogama’s laser systems are engineered for longevity and precision.

MegaWatt Lasers offers cutting-edge, Made-in-the-USA laser solutions. The ER902 Eye-Safe Miniature Solid-State Laser, designed for defense and aerospace applications, delivers high-peak power at the “eye-safe” 1.5 µm wavelength, making it ideal for range finding, LIDAR, and target designation. Built in a contaminant-free cleanroom environment and engineered for rugged, long-term reliability, this compact, ultra-low SWaP laser operates in extreme conditions, providing consistent performance in the harshest environments. With a wide operating temperature range and backed by decades of expertise from a dedicated team of physicists and engineers, the ER902 combines precision, power, and safety in a lightweight design. As a trusted partner, RPMC ensures quick shipping, no tariffs, and comprehensive support—from initial setup to ongoing maintenance—ensuring your project’s long-term success.
Further Reading: |

|
Here at RPMC lasers, we have teamed up with industry-leading partners to introduce the Kaukas & Ranger (Optogama) and ER902 (MegaWatt) into the laser designation market. For additional information, including detailed technical specifications, talk to one of our knowledgeable Product Managers today:
Talk to one of our knowledgeable Product Managers today by emailing us at info@rpmclasers.com or Contact Us with the button below!
Have questions?

 SHIPS TODAY
SHIPS TODAY