Deeper Dive into Single-Mode Fiber Output Lasers
Multimode vs Single-Mode Lasers for Raman Spectroscopy
The first question you should ask yourself when considering which type of laser to choose is whether you are doing microscopy or bulk sampling. If the answer to that question is microscopy, then you immediately should go with a single mode laser. Since the goal of any microscopy system is to produce the highest resolution image possible, the number one consideration should be how tightly can the laser beam be focused down. In optics, the M2 of a laser determines how small of a spot size can be achieved for a given microscope objective with an M2 of 1 being the best possible focus. Even though a perfect M2 of 1 can never be physically achieved, open beam single mode diode lasers can typically have a M2 < 1.5 and single mode fiber-coupled diode lasers have an M2 »1.05.
Read the full article here.
HeNe Lasers vs Diode Lasers: HeNe Laser Pros and Cons
Despite of so many good intrinsic properties, HeNe lasers often do not meet the requirements of today’s industrial environments. Industrial production lines with 24/7 operation are all about robustness and long lifetime, thus industrial instrument manufacturers tend to pay 2 to 4 times more for a laser, which has a longer life-time, is easier to replace and maintain.
The price difference from HeNe lasers mainly depend on how many parameters of semiconductor lasers have to be close to the performance of HeNe. If one needs perfect beam quality, single-mode or polarization maintaining fiber has to be used to achieve <1.05 M2, nice round beam shape and diffraction limited divergence. Reasonably good central wavelength stability can by achieved by good temperature and power stabilization of the semiconductor emitter. Most difficult and expensive to achieve is the long coherence length requirement. Most popular way of ensuring high coherence length and very stable (<5 pm) central wavelength is to apply external cavity designs (ECDL – external cavity diode laser) by using volume Bragg gratings or fiber Bragg gratings.
Read the full article here.
Laser Diode Fundamentals – Fiber Coupling
While there are countless varieties of fiber optics available on the market today, the two most important factors when discussing how the output of diode laser can be coupled into a fiber are its core size and numerical aperture. Therefore, in this blog post, we are going to first take a brief look at the physical significance of these two parameters, and why they are so crucial to laser diode coupling. In part 2 of this blog post, we will then go on to examine common fiber coupling techniques used in commercial fiber coupled laser diode packaging.
Read the full article here.
Laser Diode Fundamentals – Fiber Coupling 2
In the last blog post of our laser diode fundamentals series, we discussed the basics of fiber optics concentrating on two key parameters; core diameter and numerical aperture. We mentioned how the numerical aperture depends on the relationship between the index of the core and the cladding, and that this directly relates to the angular acceptance cone of the fiber optic. We also discussed how the core diameter in conjunction with the laser wavelength determines the spatial mode structure of the light guided through the fiber. This is why single mode fiber coupled laser diodes are far more prevalent in the infrared range then they are in the ultraviolet for example, the shorter wavelengths require smaller core diameters…
Read the full article here.
Why Should Single-Mode Fibers Have an Angle Polished?
While back reflections are definitely problematic for lasers in general, they are most problematic for single-mode lasers. Especially single-mode diode lasers. There are two primary reasons for this extreme sensitivity. As we discussed in our previous blog post titled “Laser Diode Fundamentals: Single Longitudinal Mode Diodes,” injection seeding can change the gain threshold of a laser. In that blog, we explained that by controlling the feedback into the laser you could select specific longitudinal modes. Similarly, when unwanted back reflections exist in the system, it will change the gain threshold in unintended ways and cause the longitudinal mode structure to destabilize.
Read the full article here.
Pros & Cons of Pigtailed Laser Diodes vs. Detachable Fiber-Coupled
For single-mode fibers the core diameter needs to be tiny, typically less than 10 microns, to ensure that no higher-order modes can propagate through the fiber. On the other hand, multi-mode fibers can have a wide range of core diameters ranging from 62.5 microns upward on 1 mm. Both of these fiber types are widely used with laser diodes depending on the needs of the application. For example, when the beam profile is essential, such as in microscopy, single-mode fiber is almost always preferred. By contrast in an application, such as laser cladding, where power is most important a multi-mode fiber would be the obvious choice.
Read the full article here.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your Fiber-Coupled Laser Diode
There are two main categories of fiber-coupled laser diodes, pigtailed and detachable. The pigtailed approach provides significant advantages when it comes to alignment stability, mainly when dealing with single-mode fibers which, typically have a core diameter of less than 10 microns. By comparison, it is impossible to ensure that detachable fiber-optics will line up in the same spot, each time the fiber is connected. Therefore, reducing the overall coupling efficiency of the system. However, unless the pigtail is fusion spliced to another fiber, for both pigtailed and detachable fibers, it is required that at least one end of the cable be terminated with a fiber-optic connector. As a result, it is essential to understand the different types of fiber connectors used with fiber-coupled diode lasers as well as their pros and cons.
Read the full article here.
How Can We Help?
With over 25 years experience providing single-mode fiber output lasers to OEM integrators working in different markets and applications, and 1000s of units fielded, we have the experience to ensure you get the right product for the application. Working with RPMC ensures you are getting trusted advice from our knowledgeable and technical staff on a wide range of laser products. RPMC and our manufacturers are willing and able to provide custom solutions for your unique application.
If you have any questions, or if you would like some assistance please Contact Us here. Furthermore, you can email us at info@rpmclasers.com to talk to a knowledgeable Product Manager.
Alternatively, use the filters on this page to assist in narrowing down the selection of single-mode fiber lasers for sale. Finally, head to our Knowledge Center with our Lasers 101 page and Blogs, Whitepapers, and FAQ pages for further, in-depth reading.
Finally, check out our In Stock Lasers page: This page contains all the laser products that we keep on-hand and ready to ship!
Additional Resources
Blogs:
Whitepapers:

 SHIPS TODAY
SHIPS TODAY 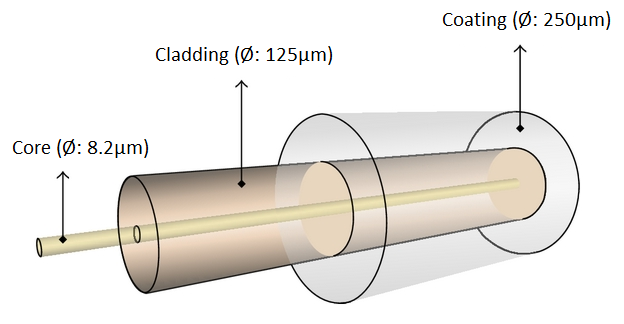 What is Single-Mode Fiber?
What is Single-Mode Fiber?




























































































































 The FL CW/CW Modulated Series of CW fiber lasers is manufactured to Telcordia standards and is suitable for various applications with powers up to 100W at 1um, 30W at 1.5um, and 40W at 2um. Available in both OEM and Turnkey formats, this series offers a variety of standard and custom configurations. Available options and configurations include narrow linewidth, single frequency outputs, C and L-band broadband sources, PM fiber options, power tunability, and high-speed trig./mod.
The FL CW/CW Modulated Series of CW fiber lasers is manufactured to Telcordia standards and is suitable for various applications with powers up to 100W at 1um, 30W at 1.5um, and 40W at 2um. Available in both OEM and Turnkey formats, this series offers a variety of standard and custom configurations. Available options and configurations include narrow linewidth, single frequency outputs, C and L-band broadband sources, PM fiber options, power tunability, and high-speed trig./mod.



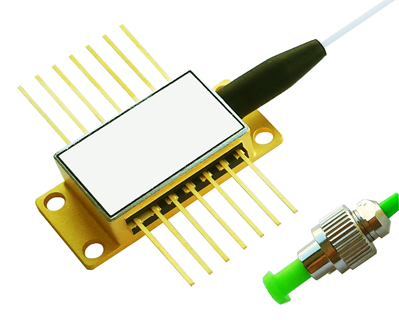 The REP series includes high-performance, tunable, single-frequency (DFB-like) diode lasers and Fabry-Perot laser diodes in wavelengths from 760nm thru 2350nm, designed to address challenges in Gas Sensing, LIDAR, Spectroscopy, and Telecom. The REP series includes high-power and narrow linewidth options, covering various product ranges at the most popular wavelengths, providing customizable units with multiple packaging options, including the Fiber coupled 14-pin butterfly, TO39 (w/TEC), and TO56.
The REP series includes high-performance, tunable, single-frequency (DFB-like) diode lasers and Fabry-Perot laser diodes in wavelengths from 760nm thru 2350nm, designed to address challenges in Gas Sensing, LIDAR, Spectroscopy, and Telecom. The REP series includes high-power and narrow linewidth options, covering various product ranges at the most popular wavelengths, providing customizable units with multiple packaging options, including the Fiber coupled 14-pin butterfly, TO39 (w/TEC), and TO56.

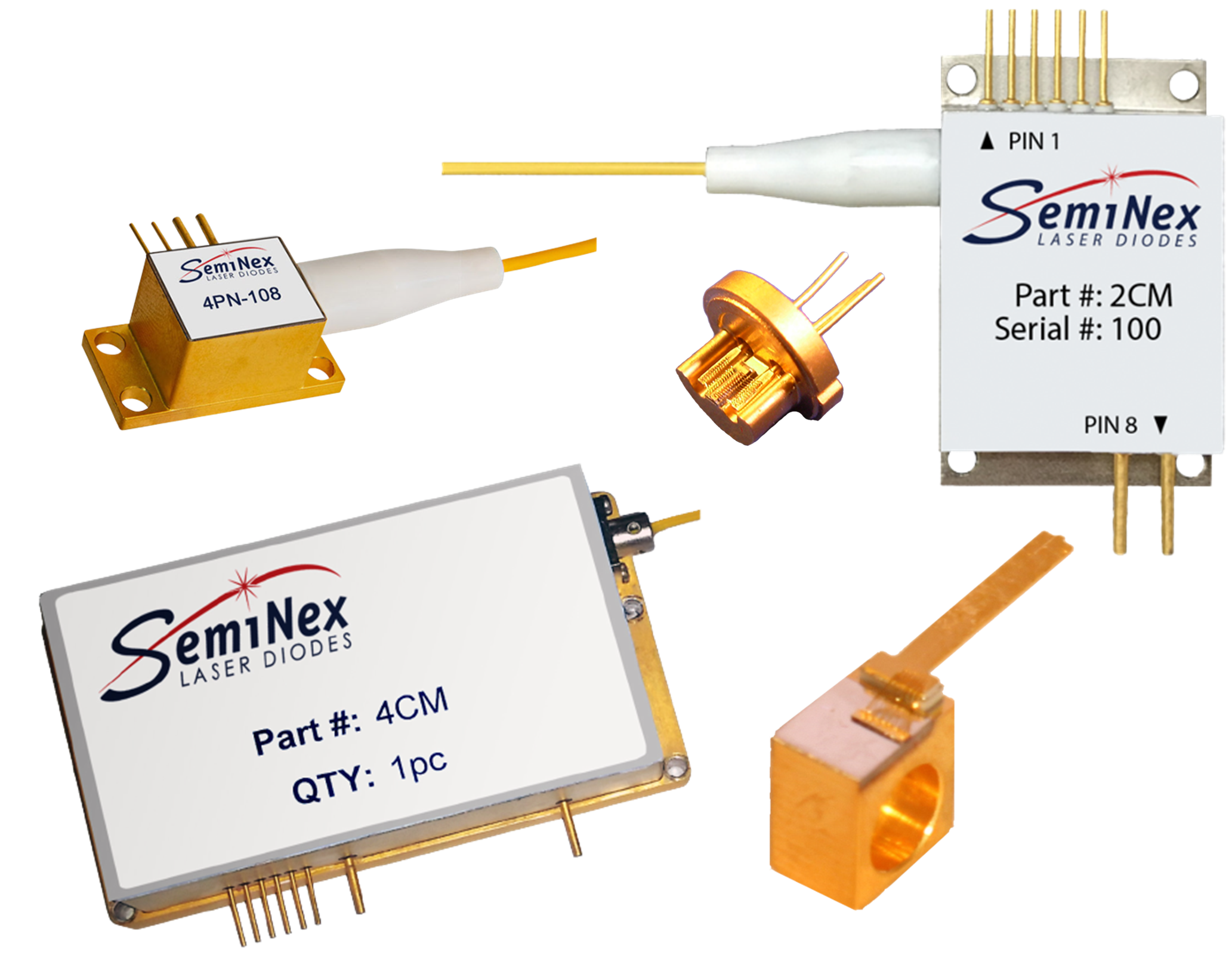 The SMX Series of US-made, high-power, thermally stable, and cost-effective InP laser diodes is available at 13XX, 14XX, 15XX, 16XX, and 19XX nm, perfect for medical, military, aerospace, LIDAR, free-space communications, and more! With a patented EPI structure, low-cost packaging, DFB & SOA configurations, ISO certified supply chain with full lifecycle traceability, focus on ease of integration, and custom design capabilities, this laser diode family is an excellent choice for reliable, high-power InP devices.
The SMX Series of US-made, high-power, thermally stable, and cost-effective InP laser diodes is available at 13XX, 14XX, 15XX, 16XX, and 19XX nm, perfect for medical, military, aerospace, LIDAR, free-space communications, and more! With a patented EPI structure, low-cost packaging, DFB & SOA configurations, ISO certified supply chain with full lifecycle traceability, focus on ease of integration, and custom design capabilities, this laser diode family is an excellent choice for reliable, high-power InP devices.