The Narrow Linewidth Lasers We Offer:
Versatile Wavelengths and Integration Options
-
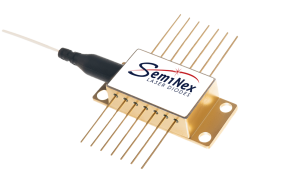
- UV-LWIR (≈263nm-17µm), power outputs up to ≈400W for diverse applications
- Single- & multimode beam profiles to fit specific system & application requirements
- Configurable options from free-space to fiber-couple, OEM to turnkey solutions

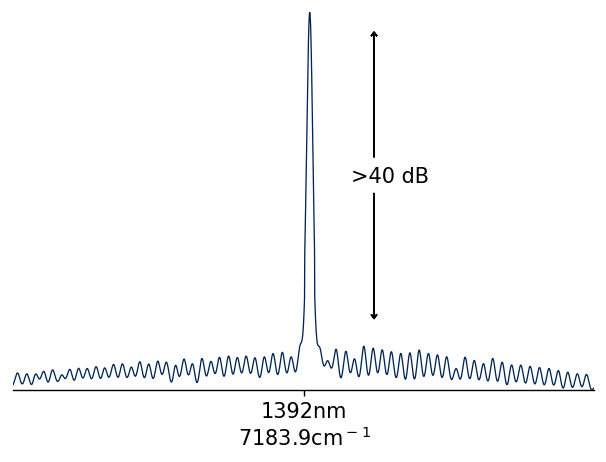
Exceptional Precision & High Spectral Purity
-
- Delivers highly stable, single-frequency light ideal for precise applications
- High spectral purity and low-noise output, minimizing contaminating frequencies
- Ideal for spectroscopy, gas sensing, and interferometry, ensuring accurate, reliable data

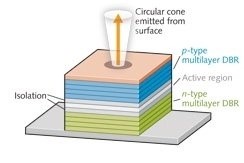
Advanced Wavelength Stabilization in a Range of Technologies
-
- DFB & VBG laser diodes w/ wavelength, temperature, current stabilization
- CW fiber, pulsed DPSS, diode lasers & HeNe with narrow linewidth performance
- Built for long-term stability, crucial for atomic clocks and sensitive measurement tasks
For nearly 30 years, RPMC’s selection of Narrow Linewidth Lasers has set the standard for affordable precision across a wide range of applications, from defense to medical, industrial, and research with 1000’s of successful units in the field. We understand that every application has unique requirements, which is why our configurable platforms are designed to offer the perfect fit for your needs. As your partner, we’re here to guide you through the selection process, ensuring that your narrow linewidth laser integrates seamlessly into your existing systems. With time-tested technology that balances power and precision, we’re committed to supporting your success every step of the way.

 SHIPS TODAY
SHIPS TODAY