SMX13XX
Laser Diode, Multimode or Single-mode, 13XX nm
Key Features:
- Wavelength: 13XX nm
- Output Power: Up to 21000mW (21W)
- High output power and dynamic range
- High efficiency
- Thermally stable
- Standard low-cost packaging
- Custom design capability
- DFB & SOA configurations available
There are many configurations and options available. If you do not see exactly what you need below, please contact us!
Need Quantities? Have a question?
POPULAR CONFIGURATIONS:
Picture |
Part Number |
Part Description |
Datasheet |
Price |
Lead Time |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
14BF-290 |
High Power SOA, 1310nm, single mode, single junction, 9 µm fiber core, FC/APC connector, 1 m long, 14 pin Butterfly Package |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |
|
14BF-450 |
High Power DFB Laser, 1310nm, single mode, 8um core diameter fiber with FC/APC connector, 14 Pin Butterfly Package |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
14BF-125 |
Singlemode Laser Diode, 1310nm, 275mW (500mW QCW), Singlemode Fiber Coupled 14-pin Butterfly package, 9µm, 0.22NA, 1m long fiber w/ FC/PC connector, PD, Thermistor, TEC |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
4CM-111 |
Laser Diode, 1310nm, 21000mW, Fiber Coupled 8-pin 4 Chip Module package, 400µm, 0.22NA, 1m long fiber w/ SMA connector, PD, Thermistor, Aiming beam |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
4PN-116 |
Laser Diode, 1320nm, 4500mW (14100mW QCW), Fiber Coupled 4-pin Module package, 105µm, 0.22NA or 0.15NA, 1m long fiber w/ SMA connector, PD |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
4PN-117 |
Laser Diode, 1375nm, 4300mW (14100mW QCW), Fiber Coupled 4-pin Module package, 105µm, 0.22NA or 0.15NA, 1m long fiber w/ SMA connector, PD |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
TO9F-111 |
Singlemode Laser Diode, 1310nm, 200mW (650mW QCW), Fiber Coupled 9mm package, 9µm, 0.22NA, 1m long fiber w/ FC/PC connector, PD, Thermistor |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
B-103 |
Laser Diode, 1310nm, 5700mW (18600mW QCW), 95µm emitter, B-mount package |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
B-123 |
Laser Diode, 1350nm, 5600mW (18600mW QCW), 95µm emitter, B-mount package |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
B-163 |
Singlemode Laser Diode, 1320nm, 800mW, 4µm emitter, B-mount package |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |
|
C-124 |
Laser Diode, 1380nm, 5600mW (15000mW QCW), 95µm emitter, C-mount package |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
C-130 |
Laser Diode, 1325nm, 5700mW (15000mW QCW), 95µm emitter, C-mount package |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |
|
COC-181 |
High Power RSOA, 1310nm, 450mW, 4µm emitter, Chip on Carrier |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
COC-288 |
High Power SOA, 1310nm, 450mW, 4µm emitter, Chip on Carrier |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
COC-289 |
High Power SOA, 1310nm, 450mW, 4µm emitter, Chip on Carrier |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
COC-290 |
High Power SOA, 1310nm, 450mW, 4µm emitter, Chip on Carrier |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |
|
C-155 |
Singlemode Laser Diode, 1320nm, 800mW (1500mW QCW), 4µm emitter, C-mount package |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |
|
TO9-184 |
Laser Diode, 1315nm, 2000mW (20000mW QCW), 95µm emitter, 9mm package, No Cap |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
TO9-185 |
Laser Diode, 1350nm, 2500mW (19000mW QCW), 95µm emitter, 9mm package, No Cap |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote | |

|
TO9-248 |
Singlemode Laser Diode, 1310nm, 400mW, 4µm emitter, 9mm package, No Cap |
|
Inquire |
Get Quote |
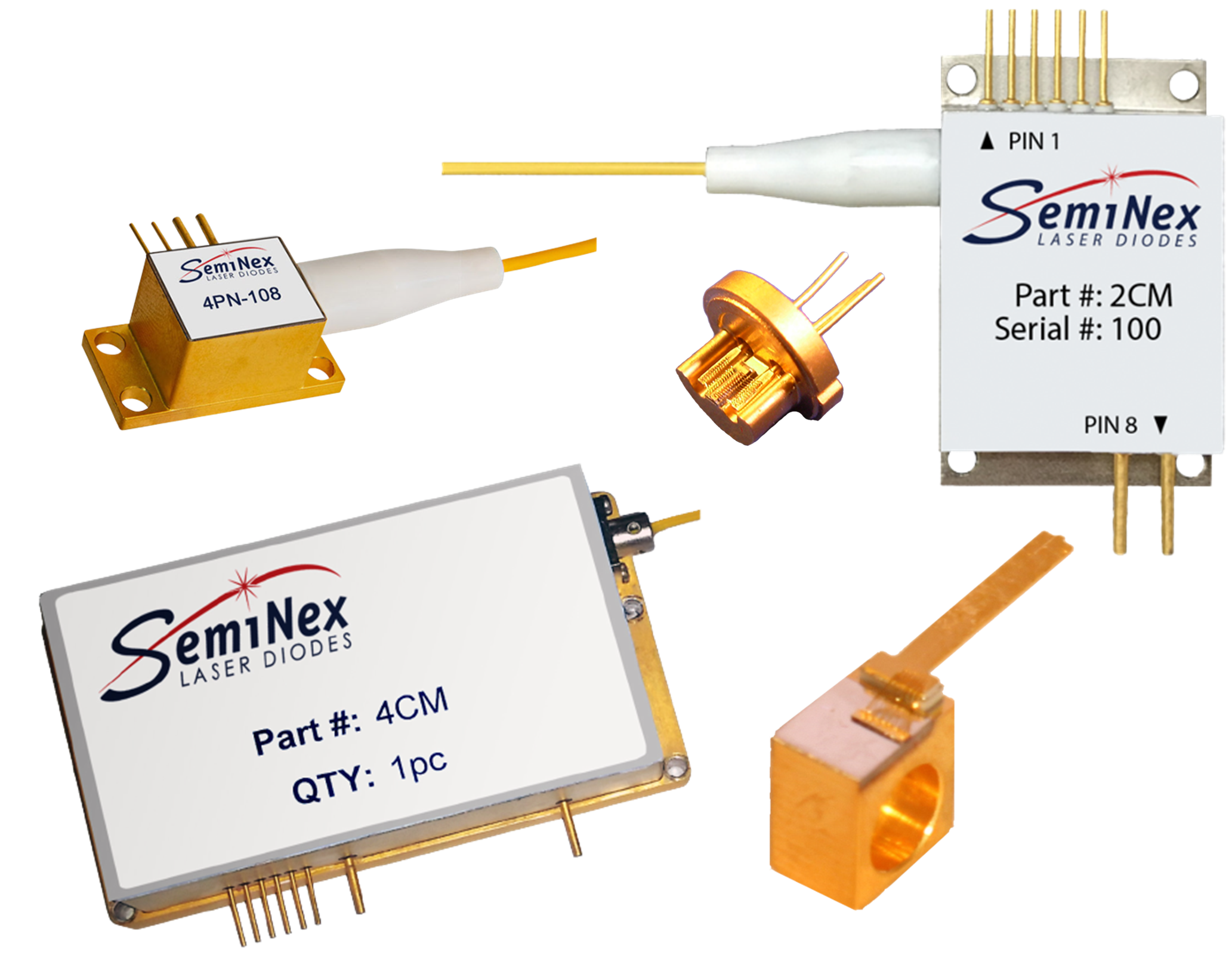
The SMX Series of US-made, high-power, thermally stable, and cost-effective InP laser diodes is available at 13XX, 14XX, 15XX, 16XX, and 19XX nm, perfect for medical, military, aerospace, LIDAR, free-space communications, and more! With a patented EPI structure, low-cost packaging, DFB & SOA configurations, ISO certified supply chain with full lifecycle traceability, focus on ease of integration, and custom design capabilities, this laser diode family is an excellent choice for reliable, high-power InP devices.
Benefits:
- Cost-Effective: standard, low-cost packaging, ideal for high-volume professional and consumer needs
- High Performance: high output power, high dynamic range, and high efficiency get you the performance you need, while conserving energy and extending lifetimes
- Thermal Stability: excellent performance over temperature range and heat resistance for consistent and reliable operation with the highest powers, even in industrial and automotive applications
- “Eye-Safe” Wavelengths: SWIR wavelengths beyond 1400nm are considered retina-safe, as they transmit well through air and glass, but are readily absorbed by water (cornea)
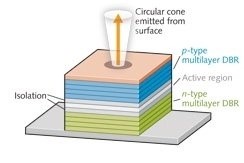
- Patented EPI Structure: High-power with single and triple-junction at elevated temperatures, ensuring consistent performance and reliability
- Technology Integration: Low-cost packages for optical, mechanical, and electrical components, simplifying assembly, reducing costs, and enhancing reliability
- Qualified Supply Chain: Rapid scaling for timely volume production, with full lifecycle traceability and ISO certification at every level of the supply chain
- Custom Design Capability: Tailored solutions, built to your specifications, when a standard solution may not suffice. Tell us what you need!
We deliver the highest available power at infrared wavelengths around 1470, 1550, and 1940 nm. When necessary, we will further optimize the design of our InP laser chips to meet our customers’ specific optical and electrical performance needs. We have several standard packages and configurations available, as well as customization options. If you do not see exactly what you are looking for, let us know! We may have a standard product that suits your needs. However, we have many options to tailor a solution that fits your specifications. Diodes, bars and packages are tested to meet customer and market performance demands.
If you have any questions or need more information, please contact us.
| Type | Fiber-Coupled – Multimode, DFB, Single Emitter, SOA, Triple-Junction |
|---|---|
| Wavelength (nm) | |
| Output power (W) | 0.200, 0.400, 0.500, 0.650, 1.5, 2.0, 4.3, 5.6, 15.0, 18.6, 19.0, 20.0, 21.0 |
| Mode | |
| Output | |
| Linewidth | |
| Package | Chip on Carrier, C-Mount, B-Mount, 9mm, Fiber Coupled, Butterfly FC |

 SHIPS TODAY
SHIPS TODAY